AirWindows
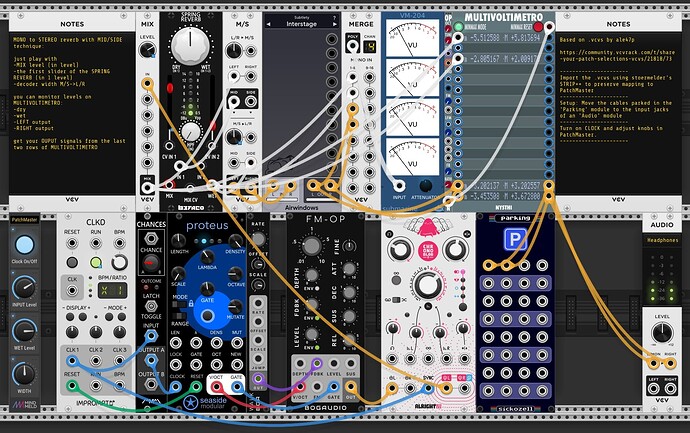
Thank you for sharing this terrific concept of converting mono signals into stereo! Here is your patch after updating the Interstage with the version by Airwindows, as suggested by @PaulPiko (Thanks!).
mono-to-stereo_reverb_with_mid-side_Airwindows version_20240731.vcvs (10.4 KB)
I then created a use case with a serene string-like sound and key controls being managed via PatchMaster. Import this .vcvs via stoermelder’s STRIP++ as described elsewhere.
Mono signal to stereo reverb_Use case_20240731.vcvs (26.0 KB)
Thank you for sharing these nine basic patch selections! Very nice and useful and educational ![]() !
!
I’m glad you like them ![]()
I was looking at your patch and this afternoon I’ll take a look at “proteus”, looks interesting
I think Proteus is great!
If you don’t know it, also take a look at the Proteus expander (ProteusX) to add even more variety using rests, transpose and a pattern bank.
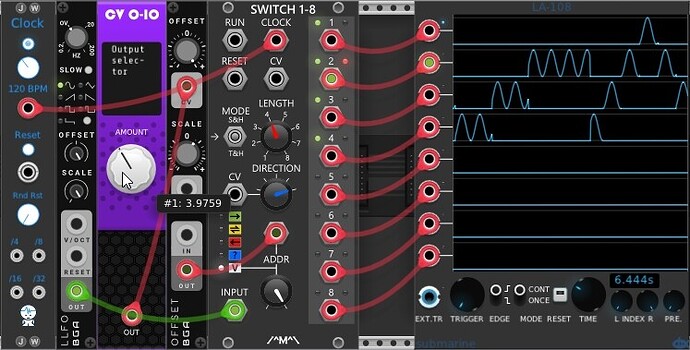
Voltage-controlled switch
A signal of 0-10V determines which output the input is routed to.
Random gate generator
With varying clock rate and pulse width.
Square LFO triggers the gate of S&H, which in turn loops back to modulate the frequency of the LFO. Offset module to control ranges. Higher S&H values yield higher clock rates.
Modified from a video by Omri Cohen.
Random gate generator_20241001.vcvs (3.9 KB)

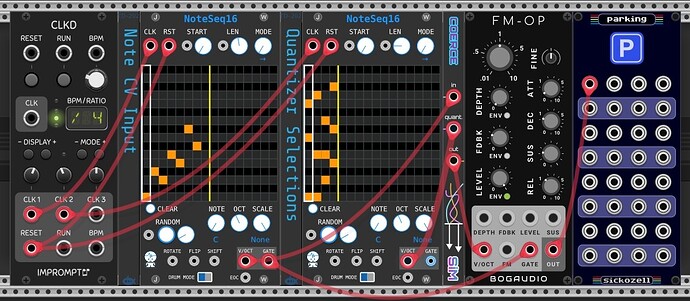
Flexible Quantizer
A user-friendly way to quantize a pitch CV input signal flexibly using Coerce by SIM. Coerce quantizes the input on its IN port to the notes fed into the QUANT port.
The pitch CV input can be mono- or polyphonic. In the example, NoteSeq16 by JW is used to generate a monophonic sequence.
The notes selected for quantization can be entire scales, chords or just a few notes. Advancing the associated NoteSeq16 switches to the next quantization template.
Allows for e.g. easily creating ‘transposed’ arpeggios with flexible quantization.
Flexible quantizer_20241005.vcvs (15.1 KB)
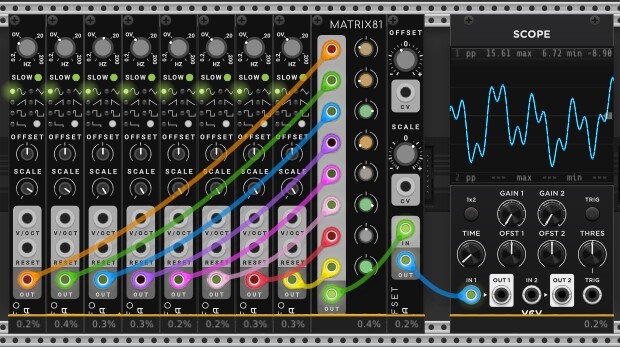
Complex custom sine-derived LFO (mono- and polyphonic versions)
A single complex LFO is created additively from up to 8 sine LFOs of different frequencies, offsets and scales. Contributions (weights) of the source LFOs are controlled in MATRIX81 (Bogaudio). Offset and ampliude of the final LFO is adjusted in OFFSET (Bogaudio).
Complex custom sine-derived LFO_monophonic_20241029.vcvs (11.0 KB)
There also is a polyphonic version of it, but it does not offer much advantage.
Complex custom sine-derived LFO_polyphonic_20241029.vcvs (8.6 KB)

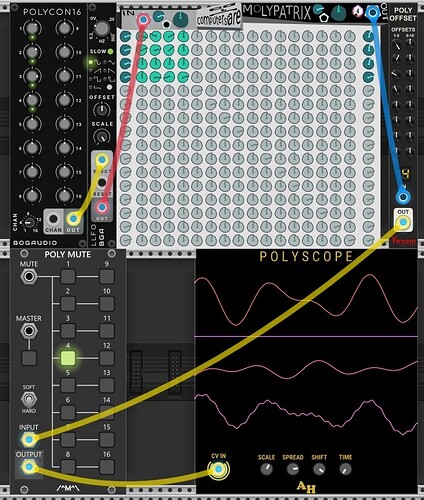
16 complex custom sine-derived LFOs (polyphonic)
Moly Patrix (computerscare) is used to create up to 16 complex LFOs by mixing up to 16 different sine LFOs of different frequencies. Results are spread across 16 channels. Use Output attenuators in Moly Patrix and knobs in Poly Offset (Venom) to scale and offset results. The optional Poly Mute (Count Modula) is used to mute individual LFOs (sets output to zero).
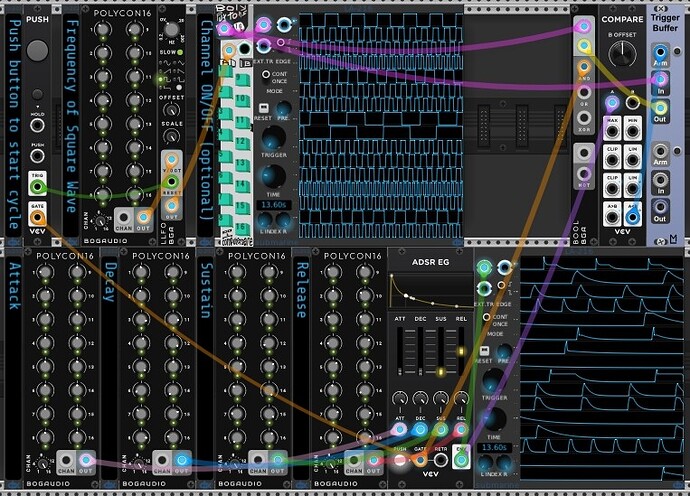
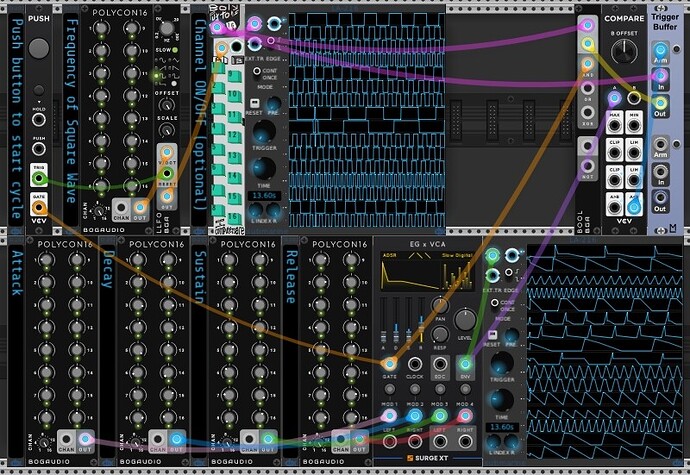
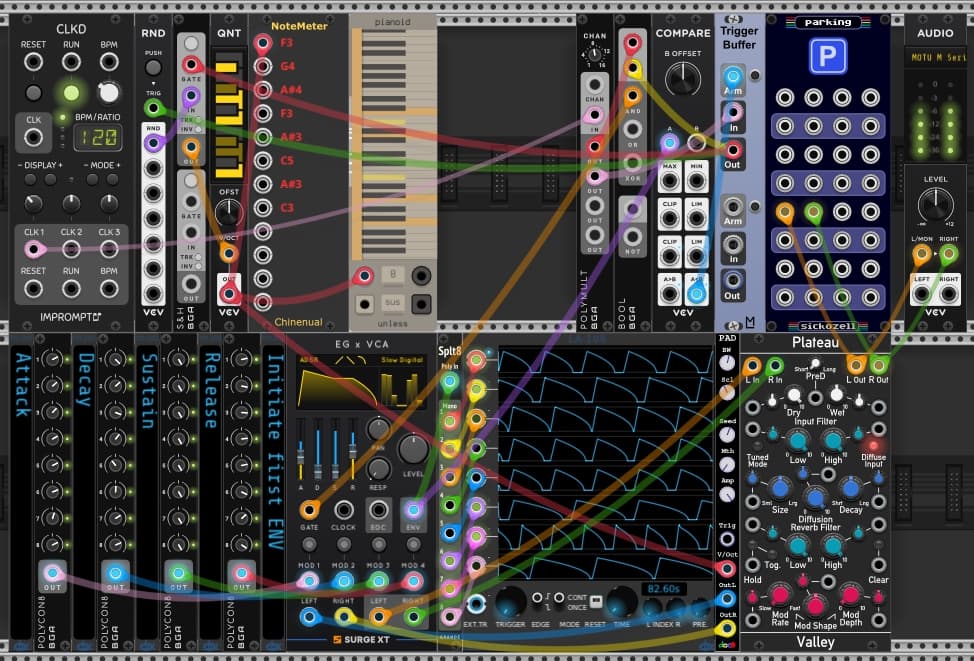
Polyphonic ADSR with cycle completion
The setup allows a new ADSR cycle to be initiated only after the prior ADSR cycle has completed.
Shown are two variants using different ADSR modules a.) ADSR EG by VCV and b.) EG x VCA by Surge XT.
To sense completion of a cycle, ADSR output is compared to a low constant value (0.01V) using Compare (VCV), which in turn arms a trigger buffer (ML Modules). The trigger is then released from the buffer upon next input.
Polyphonic ADSR with cycle completion_ADSR EG_20241113.vcvs (21.4 KB)
Polyphonic ADSR with cycle completion_EG x VCA_20241113.vcvs (24.3 KB)
As use cases, here are two examples that generate random flowing chords of 4 and 8 notes, respectively:
Use case_4-note flowing chords_EG x VCA_20241113.vcvs (25 KB)
Use case_8-note flowing chords_EG x VCA_20241113.vcvs (33.3 KB)
Single dry-wet knob for stereo audio
Controls the intensity (D/W) of an effect in a stereo audio signal with a single knob. Employs XFADE (Bogaudio) to crossfade between dry and wet signal using its MIX knob.
Stereo (L/R) channels are first merged into a polyphonic signal using MergeSplit4 (Grande), then fed into XFADE and split again afterwards by going back to MergeSplit4.
Single dry-wet knob for stereo audio_20241127.vcvs (3.3 KB)
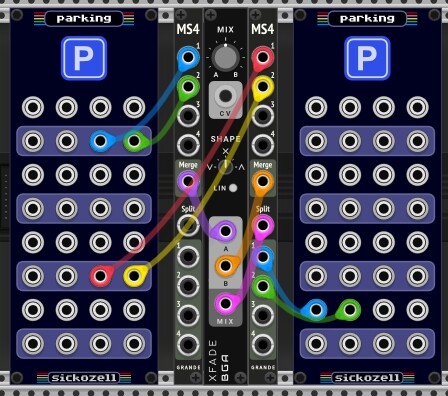
Here is a use case controlling the D/W-signal of Elastika (Sapphire):
Use case_Single dry-wet knob for stereo audio_20241127.vcvs (14.1 KB)
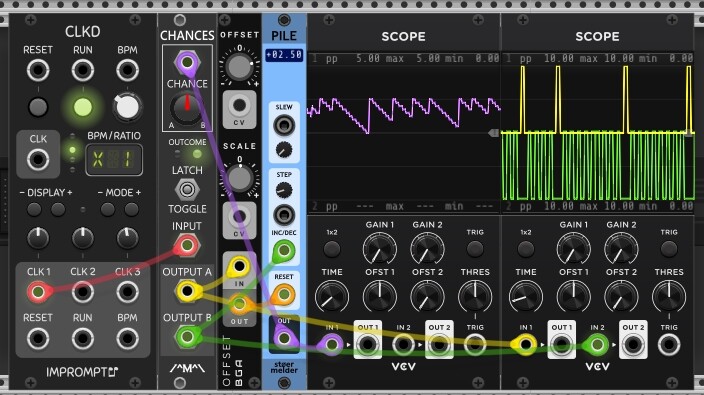
Progressively increasing chance of A over B
From a recent post:
The approach here is to progressively move the probability parameter of Chances (Count Modula) toward A with each B being triggered. stoermelder’s PILE can create a trigger-controlled decremental sequence, which can control the Chance parameter of Chances. When A is finally triggered, PILE is reset to its maximum value and the cycle starts anew.
The voltage range of the Chance knob is -5 to + 5V, so an offset is added using Offset (Bogaudio) to bring PILE’s values into a proper range.
The Step knob of PILE controls how quickly the probability for A is rising (slope). With larger values, A is triggered more frequently compared to lower values.
UPDATE: Updated to a new version, which omits the jump in the decrement curve by controlling input voltage on the Reset port of PILE.
2024-12-23_Progressively increasing chance of A over B_Improved.vcvs (6.2 KB)
[Note to @stoermelder: I have been trying the same setup with POLY-PILE, just in a polyphonic constellation, but so far couldn’t get any output at all (other than 0V) from this module. Perhaps there is something that I am missing; is the module fully functional right now?
Update on POLY-PILE: I looked into the polyphonic setup again and found that POLY-PILE only responds to increment or decrement triggers if both, INC and DEC input ports are connected. So, the module appears to be fully functional if connected correctly. As there was no signal fed into the INC port, this may be the reason why I could not get POLY-PILE to work.
Another point to consider is that the Reset port of POLY-PILE is actually monophonic, so all channels are always reset in sync, which is not useful for resetting channels independently. Hence I am currently exploring alternative ways of causing a per-channel reset, which likely will involve sending a polyphonic burst of triggers to the INC port.]
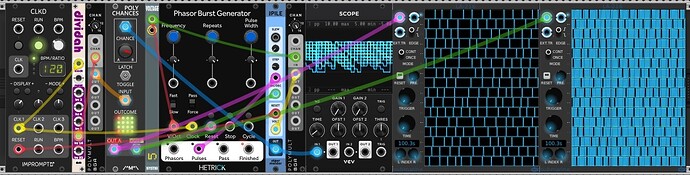
Progressively weighted Bernoulli Gate, polyphonic
The polyphonic version of the “Progressively increasing chance of A over B” patch above.
Since the Reset port of POLY-PILE is only monophonic, the module always resets all channels together, meaning they cannot be reset independently.
Therefore this patch uses a different approach: Values of POLY-PILE are reset per-channel by feeding a polyphonic salvo (burst) of rapid triggers into the (polyphonic) INC port. With this, each channel can be reset independently when the A on the respective channel is triggered.
Phase Burst Generator (HetrickCV) is used as a polyphonic burst generator, and Count Modula’s Polyphonic Bernoulli Gate as a polyphonic Bernoulli gate.
Use the Step knob on POLY-PILE to direct the decremental slope, similar to the monophonic version.
2024-12-24_Progressively increasing chance of A over B_POLYPHONIC.vcvs (11.0 KB)
Simple Bassline Generator.
For when you need a bass riff, but can’t be bothered to patch up a whole voice and sequencer. It’s a pretty standard setup but it sounds good and it’s easy to tweak (either to get new sequences or new sounds).
BasslineGenerator.vcvs (14.5 KB)
Love it! Thank you for sharing!
I wanted to share some selections I use all the time.
First is a simple polyphonic clock I use in almost every patch.
poly_lfo_clock.vcvs (2.5 KB)
The second is a virtual interface for my Launch Control XL made with Patch Master modules. It helps me get the most out of my midi mapping. You have to load it with STRIP to preserve mappings.
virtual_LCXL_factory_colors.vcvss (69.0 KB)
Hope someone finds these useful!
Thank you, very nice!
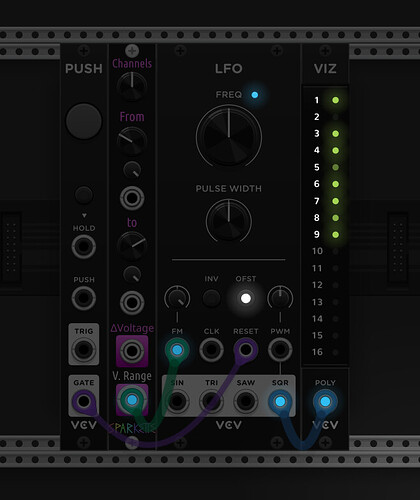
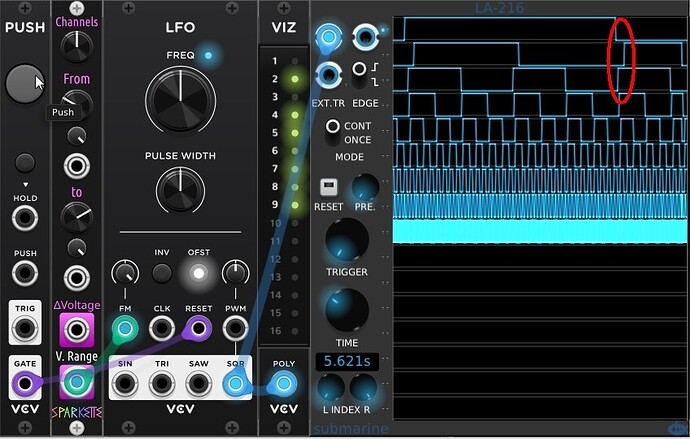
I can’t quite explain it, but it seems that on my system the clock channels in the patch go out of sync rather quickly. For example, in the pic below, Channel 2 lags behind progressively. Do you observe that, too?
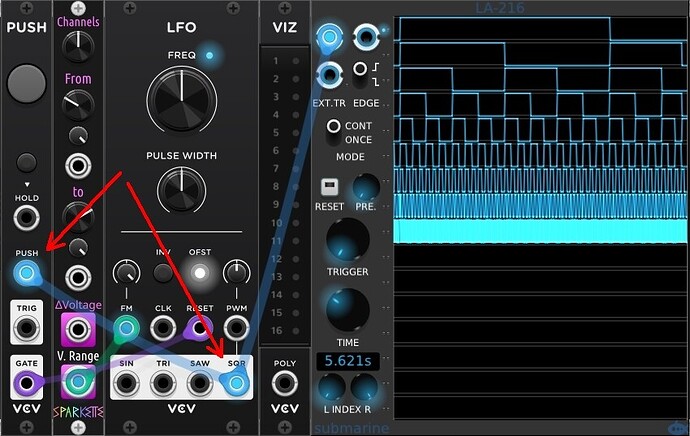
Would it make sense to regularly sync the clocks with a cable from SQR to PUSH? Since the PUSH module is only monophonic, Channel 1 (the slowest of all clocks) triggers the sync.
Any feedback would be appreciated!
Unfortunately, I do not have a Launch Control XL, so can’t use the patch selection. But it looks nice and clean for sure ![]() .
.
I think you’d be better off with a mono oscillator, a clock divider/multiplier and a merge module to get poly clocks that stay in sync. Trying to sync independent LFOs will generate timing issues for sure.
Wow. Yes it does quickly de-sync. I have probably gotten away with this so far because most of my patches have lots of off-the-grid timing. Thank you for investigating, otherwise some people may have been driven mad if they tried to use it as a regular clock. I thought I was so clever haha.